Carotid Artery Stenosis: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
Carotid artery stenosis is among such health conditions that tend to develop faintly and culminate as a severe issue. Narrowing of the carotid arteries predisposes the chances of suffering a stroke greatly since it is one of the major causes of disability and death in the world. Increasing awareness of this disease, its causes, the warning signs of this condition, and the treatment options is crucial in maintaining health of the brain in the long term. This article outlines the definition of carotid artery stenosis, its occurrence, its symptoms, and modern approaches toward its diagnosis and management.
What is Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Two major carotid arteries run through the human body and they are located on each side of the neck. They play the major role of transporting oxygenated blood through the heart to the brain, face, and neck. In case these arteries are narrowed, it results in a condition called carotid artery stenosis.
The extraction is normally caused by the formation of plaque within the walls of the artery. With time, the limited circulation of blood exposes one to the threats of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are commonly referred to as mini-strokes and more serious strokes in case of absence of treatment
How Do Carotid Arteries Get Blocked?
Atherosclerosis is the major cause of narrowing or blockage of carotid arteries. It is progressive whereby fatty materials, cholesterol, calcium, and other cell debris accumulate on the inside of the arteries. Their hardened deposits are referred to as plaque and eventually block the circulation of blood.
Several risk factors make this process more likely:
- High cholesterol that promotes fatty plaque formation
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) that strains artery walls
- Diabetes, which damages blood vessels over time
- Smoking, which accelerates injury to arteries
- Obesity and sedentary habits, leading to poor circulation
- Age, with higher risks seen in individuals above 60
- Family history of vascular disease
When asked how do carotid arteries get blocked, the simple answer is: through years of lifestyle influences, combined with genetic predisposition, leading to plaque buildup that obstructs blood flow to the brain.
Carotid Artery Stenosis Causes
Summarizing the central carotid artery stenosis causes:
- Atherosclerosis (main factor)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Genetic factors
- Advancing age
- Lack of exercise and poor dietary habits
Recognising Carotid Artery Symptoms
The importance of being aware of the symptoms of carotid artery disease is vital, as the condition may not reveal itself in any recognisable form before blood circulation to the brain is already impaired. The most widespread warning signs are connected with transient ischaemic attacks (TIAs) that may take sudden form and manifest themselves in a few hours.
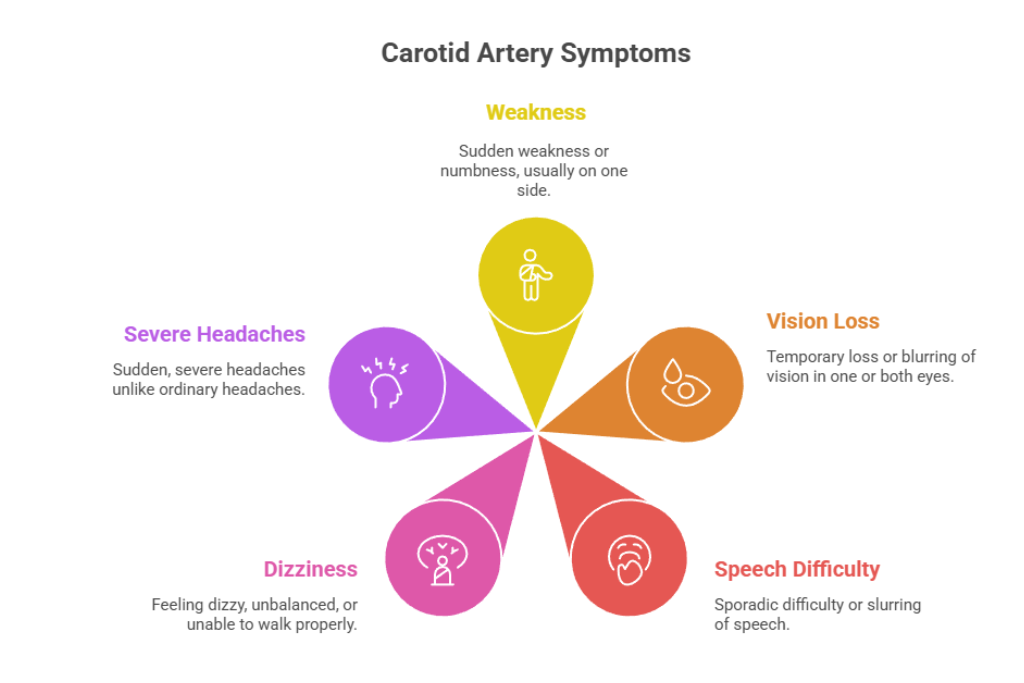
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness, numbness or arm paralysis, which is usually only on one side of the body.
- Considerable temporary loss or blurring of vision in either one or both of the eyes.
- Sporadic difficulty of speech, slurred speech, or speech comprehensibility.
- Feeling dizzy, unbalanced or unable to walk.
- Severe and sudden attacks of headaches are not similar to ordinary headaches.
These attacks are not like ordinary incidents; they must always be considered as timely warnings that they can lead to a massive stroke.
Carotid Artery Blockage Symptoms
Carotid blockage symptoms may include:
- Half-body weakness or paralysis.
- Facial drooping or numbness
- Losing track, or an abrupt inability to comprehend other people.
- Memory impairment or mental issues.
- Difficulty in walking, tripping or often lacking balance.
- Swallowing problems and speech problems.
Can Carotid Artery Disease Cause Dizziness?
Yes. Can carotid artery disease cause dizziness? The answer is yes, it tends to do so. Poor blood flow to the brain may be in the form of frequent dizziness, lightheadedness, and recurrent problems with balance. Although the causes of dizziness are diverse, individuals with risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, and others should always be detected.
Carotid Artery Aneurysm: A Related Concern
The reduction of the diameter characterises carotid artery stenosis, but at other times the artery wall is weaker and bulges out as a carotid artery aneurysm. This is a less prevalent condition that has its own risks, especially when the aneurysm breaks or it gets clots which travel to the brain.
Carotid Artery Aneurysm Symptoms
Carotid artery stenosis symptoms are as follows:
- Pain or tenderness in the neck
- A pulsating lump in the neck
- Headaches
- Vision disturbances
- Facial pain or numbness
- Difficulty swallowing
Carotid Artery Aneurysm Causes
The carotid artery aneurysm causes are similar to those leading to stenosis, such as:
- Atherosclerosis weakens the artery wall
- Chronic high blood pressure
- Trauma to the neck area
- Genetic connective tissue disorders
- Infections that compromise the arterial wall
Carotid Artery Plaque Treatment
Treatment of carotid stenosis is based on severity. In mild proceedings, medical treatment and change in lifestyle suffice. The treatment of Carotid artery plaque typically consists of:
- Medications: Antiplatelet such as aspirin or clopidogrel prevent clots; statins will lower cholesterol; antihypertensives will lower blood pressure.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, exercising, stress reduction, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Carotid Artery Blockage Treatment Diet
Making nutrition help hinder futile damage. Treatment diet involving a carotid artery blockage involves:
- Whole grains, vegetables and fruits.
- Proteins that are lean like fish and poultry.
- Nuts, seeds and fatty fish are sources of omega-3.
- Minimal saturated fats, processed meat, and fried food.
- Less salt so that blood pressure is maintained.
- Antioxidant foods, i.e., berries and greens.
Advanced Interventional Treatments
Advanced interventions are needed when narrowing becomes acute or the symptoms have become more advanced. Options include:
- Carotid Endarterectomy: A medical operation wherein a treatise is removed surgically against the artery.
- Carotid Artery Stenting: It is a less invasive procedure whereby a stent is placed to prevent the narrowing of the artery.
- Balloon Angioplasty: It involves the insertion of a balloon into the artery in order to push against plaque.
Immediate rupture of the carotid artery in case of emergencies should be treated. This can include a surgical repair or endovascular stent type that will be able to fix the blood flow pattern to avert fatal consequences or avert death.
Prevention Strategies
Carotid artery disease prevention is usually more effective in comparison to higher degree stenosis treatment. The setframes preventative measures comprise:
- Frequent medical examinations particularly above 60 years.
- Maintaining and regulating blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Eating a heart healthy, balanced diet.
- Regular physical activity
- Reifers to avoid smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Meditation/ Relaxation Management of stress.
Importance of Early Detection
Carotid stenosis can be effectively treated with early diagnosis as the key. Carotid ultrasound, CT angiographic, and MR angiography are non-invasive imaging techniques that can be utilized to identify narrowing. Tablet stroke can be avoided, preventing the likelihood of stroke significantly before the delay.
Living with Carotid Artery Stenosis
The diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis does not imply the poor quality of life. Through treatment, a significant number of patients lead normal productive lives. Management in the long-term is:
- Regularly taking medications.
- Following lifestyle advice
- Follow-up appointments.
- Being attentive to new or recurring symptoms.
Future Directions in Treatment
The study of vascular medicine is continuously developing. There are some improvements such as drug-eluting stents, improved imaging, and new cholesterol-lowering treatment. The scientists are even considering regenerative processes, including stem cell therapy and gene therapy that would make arteries stronger and less prone to plaque in the future.
Conclusion
Carotid artery stenosis is a foreseeable and silent conditions, and they may prove deadly to the stroke once it is ignored. Knowing its causes, being able to identify the symptoms of the carotid artery and being aware of its lifestyle and medical treatment options also provides people with ability to maintain their brain health safe.
Modern medicine provides various options to deal with this condition efficiently manifesting as lifestyle changes and dietary therapy to reverse carotid artery blockage and surgical treatments, endarterectomy, and stenting. Awareness and long-time response are the best countermeasures.
Mostly, a sudden weakness, dizziness or vision changes are grounds to worry, and the patient should immediately be seen. When treated early and managed with preventive medicine, patients can significantly reduce their stroke risk and maintain healthy, active lifestyles.