Brain Clot Symptoms: Early Warning Signs to Never Ignore
A brain clot is one of those emergencies where every minute matters. Early detection of the symptoms can be the difference between walking out of the hospital and experiencing long term complications. Being a stroke and vascular specialist, Dr Arvind Nanda has spent over two decades, as a researcher, at the intersection of bold initial identification and its impact on patient health. It genuinely saves lives.
Brain Clot Meaning: What You Need to Know
It is better to know what a brain clot really is before we proceed with the warning signs. The occurrence of a brain clot (also known as a cerebral thrombosis or a stroke) can be explained by a disruption or obstruction of blood flow to a section of the brain. This impediment deprives the brain of oxygen and nutrients. Several minutes later, the latter cells start perishing.
In some cases, the clot is created within the arteries of the brain (a thrombotic stroke). In other cases, it is brought to the body in a different region, most commonly the heart (an embolic stroke). Whatever the point of origin is, it is all the same: the brain is now cut off at the very source of its blood supply, and the condition is acute.
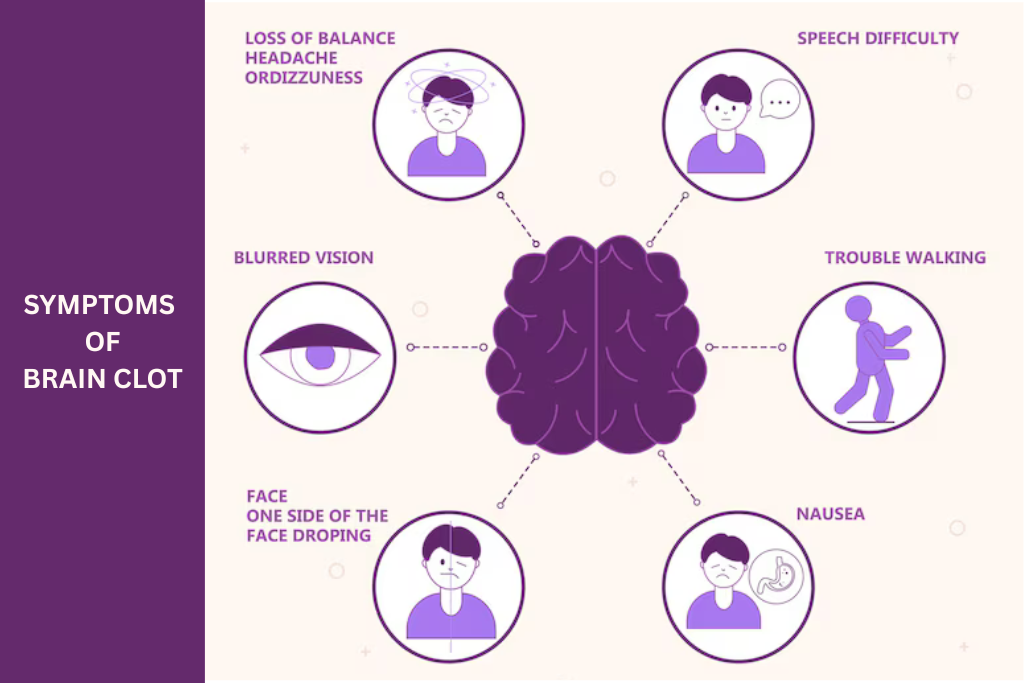
The Critical Early Warning Signs
When it comes to brain clot symptoms, time is your biggest weapon. Every passing moment increases the likelihood of permanent damage, which is why experts often say, “Time is brain.”
Sudden Severe Headache
One of the main brain clot symptoms is an abrupt headache that is explosive. According to the patients, it always feels like nothing they have ever experienced before, distinguished by a sharp, unbearable pain, which suddenly strikes them. It is not the ordinary migraine or even a sinus ache. When it hits unexpectedly and intensely, it is an indication of seeking immediate assistance.
Facial Drooping
Facial asymmetry is another sign that is easy to identify. Ask the person to smile. When one side of the face drags or fails to move as it should, it indicates that an area of the brain that controls such muscles is not getting sufficient blood.
Arm or Leg Weakness
One of the most frequent symptoms is sudden weakness or numbness of one of the arms or legs, particularly on one side of the body. You might feel heavy, find that you cannot lift one arm, or fall with no apparent cause.
Speech Difficulties
Due to the fact that the nerve clusters of the brain controlling speech are very delicate to the disrupted blood flow, the truth is that many individuals with a brain clot experience a sudden difficulty in pronouncing words easily. There may be a problem with speech, such as slurring, being slow, or jumbling. There are individuals who are unable to construct or comprehend simple sentences.
Vision Problems
Visual processing may be interfered with by a brain clot. It may be blurred vision, double vision, tunnel vision, or sudden partial blindness. It can be an indication of a decrease in the blood flow to the brain, even with a few instances of loss of sight in one eye.
Loss of Balance
Balance and coordination may then disappear overnight in case the clot has taken hold of the cerebellum or the brainstem. An individual might fall, experience dizziness, or be unable to stand straight. In case of dizziness being accompanied by other symptoms, it becomes particularly alarming.
Confusion or Cognitive Changes
Whether it is due to a clot in the brain, people may suddenly appear disoriented, confused, or unable to process basic information. This is observed by the loved ones prior to the individual realising that something is amiss.

The F.A.S.T. Method: Your Emergency Guide
A simple way to check for stroke symptoms is the F.A.S.T. rule:
- Face: Ask for a smile. Does one side droop?
- Arms: Can they raise both arms, or does one drift downward?
- Speech: Ask them to repeat a simple phrase. Does it sound unclear or strange?
- Time: If any of these signs appear, call emergency services immediately.
Risk Factors You Should Know
Some people face a higher risk than others. Age-related factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity and absence of consistent movement are factors that increase the risk of having a brain clot. Age is a cause as well, but it increases after the age of 55; not only do older people get strokes.
Heart diseases, particularly atrial fibrillation, increase the risk of the development of clots sharply. The risk is also increased by a history of past strokes or transient ischaemic attacks (TIAs).
Why Immediate Action Matters
Today, with the available treatments, such as mechanical thrombectomy, physicians are often able to remove the clot and restore the blood flow. When it comes to speed, these procedures are best. Without oxygen, the brain cells do not take long to die off. A complete recovery is more likely in the case of earlier treatment.
Don’t Wait and See
Waiting to see whether it is going to get better is one of the most damaging reactions. Symptoms of stroke will hardly find a solution without medical assistance. It can be a TIA despite the symptoms disappearing several minutes later, and it is a significant warning sign of a larger stroke in the offing.
In case you observe any symptoms, not only in you but also in a person around you, call an ambulance. Do not perpetuate yourself; postpone help.
The Bottom Line
Brain clots provide very obvious alerts: all at once, feeling weak, headache, speech difficulties, vision alterations, dizziness, and confusion. Early identification of the symptoms provides the highest probability of avoiding chronic harm. Do not forget the F.A.S.T. checklist, do not procrastinate and consider any sign of the warning as an emergency. In respect of defending the brain, every second is literally essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a brain clot and the way it is formed?
Brain clot or cerebral thrombosis is the obstruction in the blood vessels of the brain. It may develop within the brain or it may be a pathway of another part of the body. The brain cells start to die within a few minutes when blood supply is blocked hence urgent treatment is required.
Q2. What are the most prevalent common early symptoms of brain clot?
Symptoms such as sudden severe headache, weakness or numbness in one part of the body, facial drooping, slurred speech, problems with vision, loss of balance, and confusion without any explanation are common. These symptoms are usually unpredictable.
Q3. What is the speed of the manifestation of symptoms of brain clot?
They normally strike without a warning- very often in a few seconds or minutes. This sudden onset is one of the most important features which can help doctors distinguish it as compared to other diseases.
Q4. Does the brain clot have self-limiting symptoms?
They can also temporarily disappear in a transient ischemic attack (TIA), although this is also an alarming indicator. Though the symptoms may disappear, you need to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Q5. What will I do when I suspect that somebody is having a brain clot?
Use the F.A.S.T. method. Examine their speech, arms and face. In case there is a feeling that something is amiss, then call emergency services. Do not want to schlep them to the hospital.