What Is Acute Stroke: A Complete Guide to Understanding Brain Stroke

Stroke has already been sneaking up to become one of the most significant health issues in India. Many families have either seen it or heard about it. What is most disturbing about stroke is its unpredictable appearance. A person may be wonderful one moment and not able to speak, not able to move one half of his body, and not even able to remain conscious the next moment. It is termed as a ‘brain attack’ because the condition is just as serious as a heart attack is to the heart.
In India, strokes now rank as one of the significant causes of death and disability. Yet, this is the good news: it is possible to recover and have a healthy life when people are aware, recognise it fast, and treat it in time. It is time to get to know what an acute stroke is, what causes it, how to identify it, and what modern medicine has to offer in its treatment.
What Happens During an Acute Stroke?
The brain provides a central command system for the body. It requires consistent circulation of blood, oxygen, and nutrients, keeping all the cells of its body alive and active. The brain cells will begin to die within a few minutes when this supply is suddenly abandoned. The brain is not underwear or skin and may not be easily replaced; therefore, the damage may be irreversible.
An acute stroke merely indicates a stroke that is currently taking place, in its very initial phase. The urgency is emphasised through the word “acute”. When medics apply this term, they aim to make families realise that every second that passes is crucial. The quicker body circulation is reinstated, the more likely it is to save brain activity.
Types and Causes: Why Do Acute Strokes Happen?
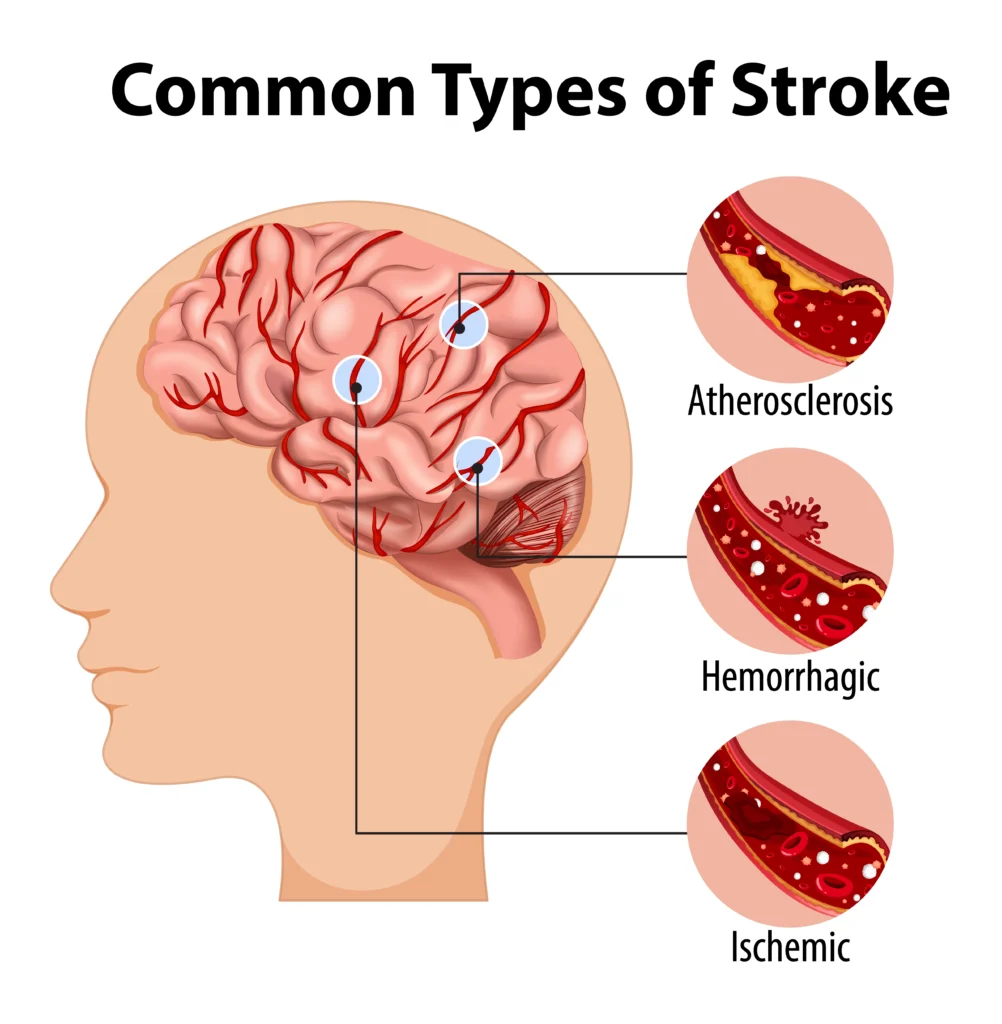
Acute Ischemic Stroke —The Commonest Form
Approximately 80 per cent of strokes are ischaemic strokes. They take place when one of the arteries delivering blood to the brain clot symptoms, Lack of oxygen also rapidly begins to kill the affected brain tissue.
How Do Blood Clots Form?
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common offenders, as it involves the accumulation of fat inside the blood vessels. Cholesterol, fat, calcium, and others create a plaque that, over time, slowly solidifies, thus making the arteries narrow. When this plaque bursts or a clot is introduced over it, then the blood supply to the brain may be blocked.
The clots may also form outside the brain. The blood clot in brain may develop within the heart in individuals with some heart issues, particularly irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation). These clots may rupture and be carried along the bloodstream, potentially blocking arteries in the head. Equally, blockages may be caused by the arteries in the neck (carotid arteries) and blocks in smaller vessels in the brain.
Less Common but Serious: Haemorrhagic Stroke
Ischaemic strokes are most prevalent, but strokes may also happen due to the bursting of a weak blood vessel in the brain. This happens to be a haemorrhagic stroke, and it results in bleeding in the brain or in areas surrounding it. It is less frequent, but when it occurs, it is commonly worse. One of the most significant causes of such strokes is high blood pressure.
Recognising the Warning Signs: How the Body Alerts Us
Stroke is one such condition, as in this case, the body provides unmistakable alert signals, though only when we can decode them.
- Sudden weakness or numbness: It occurs more frequently in one of the body parts—face, arm, or leg. One can find that they cannot raise one arm or that their smile is not balanced.
- Individuals with speech difficulties may exhibit behaviours such as constantly slurring speech, struggling to structure sentences correctly, or appearing confused during conversations.
- Visual challenges: blurred vision, visual duplicity, or immediate blindness in one or both eyes.
- Severe headache: This is a sudden and severe headache that came on, so severe that it is the worst ever experienced, accompanied by nausea or dizziness.
- Balance or coordination loss: Walking difficulty, dizziness, or falling without any reason.
The FAST test is frequently used as a method of rapid stroke identification by doctors, through which families can diagnose the disease in several minutes:
- F – Face drooping
- A – Arm weakness
- S – Speech difficulty
- T—When to call the emergency services.
Why Every Minute Matters: The Golden Hour
Once a stroke sets in, it loses millions of its cells per minute. This is the reason why physicians frequently claim that time is the brain. When treatment is initiated during the first four hours, the chart results are greater. A significant percentage of patients whose treatment is pursued at the right time come back almost wholeheartedly, whereas failure to act in good time results in paralysis in lives, speech difficulties, or even loss of life.
The golden window is very short, which is why families must take quick action. Waiting to find out whether the blood clot in brain symptoms will be cured or attempting home remedies is a waste of time. The option to always take it is to call an emergency service and seek treatment at a hospital that has adequate facilities to provide emergency stroke care.
Who Is at Risk of Stroke?
Not everyone is at the same risk; however, certain medical conditions and lifestyle habits can significantly increase the likelihood of being at risk.
Medical Risk Factors
- High blood pressure is a risk factor of paramount importance. It undercuts blood vessels with time.
- Diabetes: Affects blood vessels and escalates the chance of clotting.
- Extreme cholesterol: Causes the development of plaque in the arteries.
- Heart disease: Atrial fibrillation in particular, which has the potential to create clots.
Lifestyle and Personal Factors
- Smoking: It leads to wound complications and clots.
- Obesity and lack of exercise: Raise the chances of blood hypertension and diabetes.
- Excessive saltiness and fats in the diet: Predispose to hypertension and cholesterol.
- Age: Risk doubles after 55 years.
- Gender: Men are a little bit more exposed; however, when it comes to pregnancy and postmenopause, women are at risk.
- Family history: Genetics may be a factor, especially when the parents or siblings had a stroke.
Treatment: How Doctors Save Lives
Treatment of a stroke relies on the speed at which the patient gets to the emergency room and the nature of the stroke.
Medications
Doctors usually use thrombolytic drugs (clot-buster drugs) in case of clotting strokes as a result of ischaemia (oxygen deprivation). These drugs are effective when administered during the initial days. They break up the clot and re-establish the blood circulation before the brain tissue dies out.
Advanced Procedures
Physicians resort to specialised methods when it is not possible to heal without medicines:
- Endovascular treatment: This treatment involves a minimal intervention approach, where a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin and guided through to the brain. Physicians either clean the clot with mechanical means or administer medications to the place of blockage.
- Mechanical thrombectomy: It has established itself as the gold standard for treating large clots. A stent, a meshwork-like gadget, is inserted into the wound, pulling the clot out.
- Thrombolysis: Drugs are utilised to dissolve smaller clots. Performs optimally at the golden hours.
- Combination therapies: Doctors can treat better by using combination therapies.
Surgical Repair of Haemorrhagic Stroke
Should the bleeding cause a stroke, treatment is aimed at preventing the intracranial haemorrhage and decompressive effect on the brain. This can be open brain stroke surgery or newer methods that are minimally invasive, which vary with the case.
Benefits of Modern Stroke Treatment
The most significant benefit of the current treatment techniques lies in their significantly less invasive and more effective nature compared to the older ones. Patients subjected to endovascular procedures usually:
- Get back home in a few days rather than weeks.
- Reduced risk in terms of postoperative complications.
- Retain longer brain functions since the blood flow is reinstated in time.
- Less pain and trauma than with the traditional open surgeries.
Stroke Care in India: The Role of Specialists
In cities such as Delhi NCR, the level of stroke care is becoming more accessible. Skilled endovascular specialists, including Dr Arvind Nanda, an interventional neuroradiologist with more than 20 years of experience, are also trained in mechanical thrombectomy and removal of endovascular clots.
Failing that, AIIMS New Delhi and international training centres are in Europe and the U.S.; together with a trained doctor, Dr Nanda, and his team, they offer 24/7 emergency stroke specialist services. This incorporates the idea of rapid imaging, immediate diagnosis, and a team approach that includes the neurologists, radiologists, and critical care doctors. Previously unseen numbers of lives are being saved because of the availability of such facilities.
Final Thoughts
The acute stroke is among the most critical medical emergencies, yet it does not have to be a tragedy. When every patient is well-informed, acts swiftly, and has easy access to modern-day treatment, many of them would be in a position to heal completely and lead an everyday life.
When leaving a message, it’s essential to remember that every second counts. The awareness of the signs, prompt assistance, and directing to a specialised hospital may result in disability and recovery, respectively.
Stroke is critical, but through knowledge and preparedness, fewer effects may be experienced. They claim that educated and prepared families are much better prepared to save their loved ones in the event of a brain attack.